Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Horii, Yuta; Hirooka, Shun; Uno, Hiroki*; Ogasawara, Masahiro*; Tamura, Tetsuya*; Yamada, Tadahisa*; Furusawa, Naoya*; Murakami, Tatsutoshi; Kato, Masato
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 588, p.154799_1 - 154799_20, 2024/01
Times Cited Count:1 Percentile:68.31(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)The thermal conductivities of near-stoichiometric (U,Pu,Am)O doped with Nd
doped with Nd O
O /Sm
/Sm O
O , which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT)
, which is major fission product (FP) generated by a uranium-plutonium mixed oxides (MOX) fuel irradiation, as simulated fission products are evaluated at 1073-1673 K. The thermal conductivities are calculated from the thermal diffusivities that are measured using the laser flash method. To evaluate the thermal conductivity from a homogeneity viewpoint of Nd/Sm cations in MOX, the specimens with different homogeneity of Nd/Sm are prepared using two kinds of powder made by ball-mill and fusion methods. A homogeneous Nd/Sm distribution decreases the thermal conductivity of MOX with increasing Nd/Sm content, whereas heterogeneous Nd/Sm has no influence. The effect of Nd/Sm on the thermal conductivity is studied using the classical phonon transport model (A+BT) . The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C
. The dependences of the coefficients A and B on the Nd/Sm content (C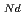 and C
and C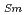 , respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70
, respectively) are evaluated as: A(mK/W)=1.70  10
10 + 0.93C
+ 0.93C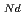 + 1.20C
+ 1.20C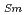 , B(m/W)=2.39
, B(m/W)=2.39  10
10 .
.
Nauchi, Yasushi*; Nomi, Takayoshi; Suzuki, Risa; Kosuge, Yoshihiro*; Shiba, Tomooki; Takada, Akira*; Kaburagi, Masaaki; Okumura, Keisuke
Proceedings of International Topical Workshop on Fukushima Decommissioning Research (FDR2022) (Internet), 4 Pages, 2022/10
Yanagisawa, Hiroshi
JAEA-Technology 2021-023, 190 Pages, 2021/11
Computational analyses on nuclear criticality characteristics were carried out for heterogeneous lattice systems composed of water moderator and fuel rods utilized in low-power research and test reactors, in which the depletion of fuel due to burnup is relatively small, by using the continuous-energy Monte Carlo code MVP Version 2 with the evaluated nuclear data library JENDL-4.0. In the analyses, the minimum critical number of fuel rods was evaluated using calculated neutron multiplication factors for the heterogeneous systems of the uranium dioxide fuel rod in the Static Experiments Critical Facility (STACY) and the Tank-type Critical Assembly (TCA), and the uranium-zirconium hydride fuel rod in the Nuclear Safety Research Reactor (NSRR). In addition, six sorts of the ratio of reaction rates, which are components of neutron multiplication factors, were calculated in the analyses to explain the variation of neutron multiplication factors with the ratio of water moderator to fuel volume in a unit fuel rod cell. Those results of analyses are considered to be useful for the confirmation of reasonableness and validity of criticality safety measures as data showing criticality characteristics for water-moderated heterogeneous lattice systems composed of the existing fuel rods in research and test reactors, of which criticality data are not sufficiently provided by the Criticality Safety Handbook.
Kokusen, Junya; Akasaka, Shingo*; Shimizu, Osamu; Kanazawa, Hiroyuki; Honda, Junichi; Harada, Katsuya; Okamoto, Hisato
JAEA-Technology 2020-011, 70 Pages, 2020/10
The Uranium Enrichment Laboratory in the Japan Atomic Energy Agency (JAEA) was constructed in 1972 for the purpose of uranium enrichment research. The smoke emitting accident on 1989 and the fire accident on 1997 had been happened in this facility. The research on uranium enrichment was completed in JFY1998. The decommissioning work was started including the transfer of the nuclear fuel material to the other facility in JFY2012. The decommissioning work was completed in JFY2019 which are consisting of removing the hood, dismantlement of wall and ceiling with contamination caused by fire accident. The releasing the controlled area was performed after the confirmation of any contamination is not remained in the target area. The radioactive waste was generated while decommissioning, burnable and non-flammable are 1.7t and 69.5t respectively. The Laboratory will be used as a general facility for cold experiments.
Task Force on Writing Textbook of Nuclear Fuel Materials
JAEA-Review 2020-007, 165 Pages, 2020/07
The present textbook was written by Task Force on Writing Textbook of Nuclear Fuel Materials at the Nuclear Science Research Institute in order to improve technological abilities of engineers and researchers who handle nuclear fuel materials. The taskforce consists of young and middle class engineers each having certification for chief engineer of nuclear fuel. The present textbook mainly deals with uranium and plutonium, and shows their nuclear properties, physical and chemical properties, and radiation effects on materials and human body. It also presents basic matters for safety handling of nuclear fuel materials, such as handling of nuclear fuel materials with hood and glovebox, important points in storage and transportation of nuclear fuel materials, radioactive waste management, radiation safety management, and emergency management. Furthermore, incident cases at domestic and foreign nuclear fuel materials facilities are compiled to learn from the past.
Ikeuchi, Hirotomo; Yano, Kimihiko; Washiya, Tadahiro
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(6), p.704 - 718, 2020/06
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:59.94(Nuclear Science & Technology)To suggest efficient process of the fuel debris treatment after the retrieval from the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F), thorough investigation is indispensable on potential source of U in the fuel debris. Estimation on the fuel debris accumulated in the reactor pressure vessel is specifically important due to its limited accessibility. The present study aims to estimate the chemical forms of U in the in-vessel fuel debris, especially in the minor phases such as metallic phases, by performing the thermodynamic calculation considering the material relocation and changing environment during the accident progression in the 1F Unit 2. Input conditions for the thermodynamic calculation such as composition, temperature, and oxygen amount were assumed mainly based on the results of severe accident analysis. The chemical form of U varied depending on the local amount of Fe and O. In regions of low steel content, the U-containing metallic phase was dominated by  -(Zr,U)(O), while regions of high steel content were dominated by Fe
-(Zr,U)(O), while regions of high steel content were dominated by Fe (Zr,U) (Laves phase). A few percent of U was transferred to the metallic phases under reducing conditions, raising challenging issues on the chemical removal of nuclear material from fuel debris.
(Zr,U) (Laves phase). A few percent of U was transferred to the metallic phases under reducing conditions, raising challenging issues on the chemical removal of nuclear material from fuel debris.
Fukushima, Masahiro; Goda, J.*; Oizumi, Akito; Bounds, J.*; Cutler, T.*; Grove, T.*; Hayes, D.*; Hutchinson, J.*; McKenzie, G.*; McSpaden, A.*; et al.
Nuclear Science and Engineering, 194(2), p.138 - 153, 2020/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:61.18(Nuclear Science & Technology)To validate lead (Pb) nuclear cross sections, a series of integral experiments to measure lead void reactivity worth was conducted systematically in three fast spectra with different fuel compositions on the Comet critical assembly of the National Criticality Experiments Research Center. Previous experiments in a high-enriched uranium (HEU)/Pb and a low-enriched uranium (LEU)/Pb systems had been performed in 2016 and 2017, respectively. A follow-on experiment in a plutonium (Pu)/Pb system has been completed. The Pu/Pb system was constructed using lead plates and weapons grade plutonium plates that had been used in the Zero Power Physics Reactor (ZPPR) of Argonne National Laboratory until the 1990s. Furthermore, the HEU/Pb system was re-examined on the Comet critical assembly installed newly with a device that can guarantee the gap reproducibility with a higher accuracy and precision, and then the experimental data was re evaluated. Using the lead void reactivity worth measured in these three cores with different fuel compositions, the latest nuclear data libraries, JENDL 4.0 and ENDF/B VIII.0, were tested with the Monte Carlo calculation code MCNP version 6.1. As a result, the calculations by ENDF/B-VIII.0 were confirmed to agree with lead void reactivity worth measured in all the cores. It was furthermore found that the calculations by JENDL 4.0 overestimate by more than 20% for the Pu/Pb core while being in good agreements for the HEU/Pb and LEU/Pb cores.
Shimada, Taro; Takubo, Kazuya*; Takeda, Seiji; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji
Progress in Nuclear Science and Technology (Internet), 5, p.183 - 187, 2018/11
After fuel debris is removed from the reactor containment vessel at Fukushima Daiichi NPS (1F) and collected in waste containers in the future, the waste containers will be disposed at a deep geological repository. The uranium inventory and uranium-235 ( U) enrichment of the fuel debris are larger than those of high-level vitrified wastes which are produced from liquid waste during reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels. Therefore, there is a possibility not to be excluded that a criticality occurs in the geological media where the uranium precipitates at the far-field from the repository, after the uranium located in the repository is dissolved by groundwater. In this study, we calculated the quantity of uranium precipitated at the natural barrier, and studied dimension of uranium deposited in the natural barrier and carried out the criticality analysis.
U) enrichment of the fuel debris are larger than those of high-level vitrified wastes which are produced from liquid waste during reprocessing of spent nuclear fuels. Therefore, there is a possibility not to be excluded that a criticality occurs in the geological media where the uranium precipitates at the far-field from the repository, after the uranium located in the repository is dissolved by groundwater. In this study, we calculated the quantity of uranium precipitated at the natural barrier, and studied dimension of uranium deposited in the natural barrier and carried out the criticality analysis.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2016-005, 40 Pages, 2016/05
Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) method is an attractive technique because real-time, in-situ and remote elemental analysis is possible without any sample preparation. The LIBS technique can be applied for analyzing elemental composition of samples under severe environments such as the estimation of impurities in the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the detection of fuel debris in the post-accident nuclear core reactor of TEPCO Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant. For applying LIBS to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is indispensable to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). In the present study, an echelle spectrometer with a resolving power of 50,000 was employed to identify spectra of natural uranium of wavelength ranging from 470 to 670 nm. The 173 atomic spectra and 119 ionic spectra can be identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
Akaoka, Katsuaki; Oba, Masaki; Miyabe, Masabumi; Otobe, Haruyoshi; Wakaida, Ikuo
JAEA-Research 2015-012, 48 Pages, 2015/10
It is important to analyze the next generation nuclear fuel material containing minor actinide (MA) and the fuel debris generated at the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station. Therefore, the remote analysis for nuclear fuel materials using Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) is studied. For applying Laser Induced Breakdown Spectroscopy (LIBS) to the analysis of nuclear fuel materials, it is very important to identify the emission spectrum and its intensity on impurities intermingled within complex emission spectra of matrix elements such as uranium (U) and plutonium (Pu). Then, the high resolution spectra of natural uranium of wavelength region of 350-470 nm are measured using LIBS, 247 atomic spectra and 294 single ion spectra were identified. We have confirmed that the measured wavelength and oscillator strength of spectra are consistent with published values.
 and (U,Zr)O
and (U,Zr)O solid solution using MoCl
solid solution using MoCl
Sato, Takumi; Shibata, Hiroki; Hayashi, Hirokazu; Takano, Masahide; Kurata, Masaki
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 52(10), p.1253 - 1258, 2015/10
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:45.66(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to explore the applicability of the chlorination by MoCl as a potential pretreatment technique for waste treatment of fuel debris by pyrochemical methods, chlorination experiments of UO
as a potential pretreatment technique for waste treatment of fuel debris by pyrochemical methods, chlorination experiments of UO and (U
and (U Zr
Zr )O
)O simulated fuel debris were carried out in two steps: the first one is a chlorination reaction by homogeneous heating, the second one is a volatilization of molybdenum by-product by heating under temperature gradient condition. Most of UO
simulated fuel debris were carried out in two steps: the first one is a chlorination reaction by homogeneous heating, the second one is a volatilization of molybdenum by-product by heating under temperature gradient condition. Most of UO and (U
and (U Zr
Zr )O
)O powder were converted to UCl
powder were converted to UCl or UCl
or UCl and ZrCl
and ZrCl mixture at 573 K, respectively. In the case of (U
mixture at 573 K, respectively. In the case of (U Zr
Zr )O
)O sintered particle, most of sample was converted to the chlorides because the products evaporated and be separated from sample surface at 773 K, while only the surface of the sample disk was converted to the chlorides at 573 and 673 K. Most of molybdenum by-product and ZrCl
sintered particle, most of sample was converted to the chlorides because the products evaporated and be separated from sample surface at 773 K, while only the surface of the sample disk was converted to the chlorides at 573 and 673 K. Most of molybdenum by-product and ZrCl were separated from UCl
were separated from UCl by volatilization at 573 K.
by volatilization at 573 K.
Asakura, Toshihide; Hotoku, Shinobu; Ban, Yasutoshi; Matsumura, Masakazu; Morita, Yasuji
Journal of Nuclear and Radiochemical Sciences, 6(3), p.271 - 274, 2005/12
Tc extraction and separation experiments were performed basing on PUREX technique with using spent UO fuel with burn-up of 44 GWd/t. The experimental results were examined with performing calculations by a simulation code ESSCAR (Extraction System Simulation Code for Advanced Reprocessing). It was demonstrated that Tc can be almost quantitatively extracted from a dissolver solution and that Tc can also be almost quantitatively recovered by scrubbing. Further, it was clearly presented from the calculation results of ESSCAR that the extraction mechanism of Tc is dominated by the synergistic effect of Zr and U.
fuel with burn-up of 44 GWd/t. The experimental results were examined with performing calculations by a simulation code ESSCAR (Extraction System Simulation Code for Advanced Reprocessing). It was demonstrated that Tc can be almost quantitatively extracted from a dissolver solution and that Tc can also be almost quantitatively recovered by scrubbing. Further, it was clearly presented from the calculation results of ESSCAR that the extraction mechanism of Tc is dominated by the synergistic effect of Zr and U.
Kokusen, Junya; Seki, Masakazu; Abe, Masayuki; Nakazaki, Masato; Kida, Takashi; Umeda, Miki; Kihara, Takehiro; Sugikawa, Susumu
JAERI-Tech 2005-004, 53 Pages, 2005/03
This report presents operating records of dissolution of uranium dioxide and concentration of uranyl nitrate solution and acid removal, which have been performed from 1994 through 2003, for the purpose of feeding 10% and 6% enriched uranyl nitrate solution fuel to Static Experimental Critical Facility(STACY) and Transient Experimental Critical Facility(TRACY) in Nuclear Fuel Safety Engineering Facility(NUCEF).
Tatematsu, Kenji; Sato, Osamu
JAERI-Research 2004-024, 35 Pages, 2005/01
Many scenarios were defined for future development of nuclear power generation and fuel cycle systems in Japan. These scenarios were quantitatively analyzed from the viewpoint of plutonium recycling, natural uranium consumption, stock of spent fuel, etc. Following findings were obtained from the analysis. RMWRs will contribute to control the uranium consumption at certain finite levels if net conversion ratio (CR) is kept higher than 1.0. However, since RMWRs do not have an excellent breeding performance in comparison with FBRs, their effect is very sensitive to the conditions on fuel recycling processes. Judging from the results of analysis using a RMWR design with gross CR 1.06, it would be necessary for RMWRs to have net CR 1.04 in order to replace enriched uranium fuelled LWRs by around the year 2200, and thereby to keep ultimate natural uranium consumption at rather low levels. This can be achieved by controlling fuel duration time outside reactors to shorter than 4 years or 6 years, when total loss of plutonium during the processes of recycling is 1.0% or 0.2%, respectively.
Mineo, Hideaki; Isogai, Hikaru; Morita, Yasuji; Uchiyama, Gunzo*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 41(2), p.126 - 134, 2004/02
Times Cited Count:7 Percentile:45.06(Nuclear Science & Technology)A simple equation was proposed for the dissolution rate of spent LWR fuel, of which the change in the dissolution area was estimated by taking into account of the area of the cracks occurring due to thermal shrinkage of the pellets during irradiation. The applicability of proposed equation was examined using LWR fuel dissolution test results in the present study as well as the results obtained by other workers. The equation showed good agreements with the dissolution test results obtained from spent fuel pellets and pulverized spent fuel. It was indicated that the proposed equation was simple and would be useful for the prediction of dissolution of spent LWR fuels. However, the initial effective dissolution area, the parameter of the equation, was found to depend on the temperature, which could not be explained by the proposed equation. Further studies on the role of other factors affecting dissolution rate, such as nitrous acid, in the dissolution of spent fuel was required.
Ando, Masaki; Nakano, Yoshihiro; Okajima, Shigeaki; Kawasaki, Kenji
Journal of Nuclear Materials, 319, p.126 - 130, 2003/06
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Materials Science, Multidisciplinary)Doppler effect experiments on resonance materials for ROX fuels were carried out to examine the calculation accuracy in the intermediate neutron spectrum using Fast Critical Assembly (FCA) at Japan Atomic Energy Research Institute. This study is the second phase of a series of the Doppler effect experiments on the resonance materials, which is following the measurements in the fast neutron spectrum. The Doppler effect was measured as the sample reactivity change between the heated and unheated samples. The cylindrical samples of the resonance materials such as erbium (Er), tungsten (W) and thorium (ThO ) were used. The sample was heated up to 800
) were used. The sample was heated up to 800 C at the center of the FCA core. The Doppler effect measurements were analyzed using the SRAC 95 code system with the use of JENDL 3.2. The calculated values agreed with the experiment within the experimental error for the W and ThO
C at the center of the FCA core. The Doppler effect measurements were analyzed using the SRAC 95 code system with the use of JENDL 3.2. The calculated values agreed with the experiment within the experimental error for the W and ThO samples, while the calculation overestimated the experiment for the Er sample about 10 %.
samples, while the calculation overestimated the experiment for the Er sample about 10 %.
Sasajima, Hideo; Sugiyama, Tomoyuki; Nakamura, Takehiko; Fuketa, Toyoshi; Uetsuka, Hiroshi
Proceedings of 7th International Topical Meeting on Research Reactor Fuel Management (ENS RRFM2003), p.109 - 113, 2003/03
Uranium-zirconium hydride (U-ZrHx) fuel has been widely utilized in the world as TRIGA reactor fuel. In order to obtain the fuel performance data under accident conditions and to enhance accountability of the safety assessment of the reactors using the fuel, irradiation tests under power burst type accident conditions have been conducted in the NSRR. Five pulse irradiation tests have been performed at peak fuel enthalpies ranging from 187 J/g to 483 J/g. Cladding surface temperature increased rapidly at the pulse and DNB occurred in peak fuel enthalpy over 187 J/g in the tests. The DNB occurred at lower fuel enthalpy in the U-ZrH1.6 fuel than in the UO fuel rods. The rod internal pressure rose up to as high as 1MPa in the transient heating tests, suggesting considerable release of the hydrogen decomposed from the fuel. The peak pressure was lower than equilibrium hydrogen pressure of 1.5MPa at the peak temperature, suggesting the transient effect. Considerable PCMI was observed in the tests, through cladding elongation up to 3.3 mm synchronized to the pellet stack deformation.
fuel rods. The rod internal pressure rose up to as high as 1MPa in the transient heating tests, suggesting considerable release of the hydrogen decomposed from the fuel. The peak pressure was lower than equilibrium hydrogen pressure of 1.5MPa at the peak temperature, suggesting the transient effect. Considerable PCMI was observed in the tests, through cladding elongation up to 3.3 mm synchronized to the pellet stack deformation.
Tabata, Toshio; Nagao, Yoshiharu; Komukai, Bunsaku; Naka, Michihiro; Takeda, Takashi*; Fujiki, Kazuo
JAERI-Tech 2002-100, 108 Pages, 2003/01
After the investigation of the new core arrangement for the JMTR reactor in order to enhance the fuel burn-up and consequently extend the operation period, the "improved LEU core" that utilized 2 additional fuel elements instead of formerly installed reflector elements, was adopted. This report describes the results of the thermal-hydraulic analysis of the improved LEU core as a part of safety analysis for the licensing. The analysis covers steady state, abnormal operational transients and accidents, which were described in the annexes of the licensing documents as design bases events. Calculation conditions for the computer codes were conservatively determined based on the neutronic analysis results and others. The results of the analysis, that revealed the safety criteria were satisfied on the fuel temperature, DNBR and primary coolant temperature, were used in the licensing. The operation license of the JMTR with the improved LEU core was granted in March 2001, and the reactor operation with new core started in November 2001 as 142nd operation cycle.
Mineo, Hideaki; Suzuki, Tadashi; Morita, Yasuji
Proceedings of 2nd International Symposium on Supercritical Fluid Technology for Energy and Environment Applications (Super Green 2003), p.334 - 338, 2003/00
Behavior of spent nuclear fuel in subcritical water was investigated to look at the feasibility of fission-products (FPs) separation without organic solvent. The study employed unirradiated UO particles simulating spent fuel burned up to 45,000MWdt
particles simulating spent fuel burned up to 45,000MWdt , which includes FP elements in oxide form: Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd and Sm. Also, alloy particles consisted of Mo, Ru, Rh and Pd were prepared to simulate the metallic phase of FP. 12.728 g of the fuel and 52 mg of the alloy were placed in a 10 ml pressure vessel, where subcritical water was fed. The temperature was 523, 573, 623 and 663K, while the pressure was kept at 29MPa. Dissolved fraction decreased with elevating temperature. It was found that more than 5% of Ba, Mo and Pr were respectively dissolved. The dissolved fraction of Sr and Rh were about 1%, and about 0.3% for Zr. La, Ce, Nd and Sm, indicated almost the same result as U, which was about 0.1%. It was suggested that the subcritical water could separate portion of FP. Further study would be carried out with smaller-sized fuel.
, which includes FP elements in oxide form: Sr, Zr, Mo, Ru, Rh, Pd, Ag, Ba, La, Ce, Pr, Nd and Sm. Also, alloy particles consisted of Mo, Ru, Rh and Pd were prepared to simulate the metallic phase of FP. 12.728 g of the fuel and 52 mg of the alloy were placed in a 10 ml pressure vessel, where subcritical water was fed. The temperature was 523, 573, 623 and 663K, while the pressure was kept at 29MPa. Dissolved fraction decreased with elevating temperature. It was found that more than 5% of Ba, Mo and Pr were respectively dissolved. The dissolved fraction of Sr and Rh were about 1%, and about 0.3% for Zr. La, Ce, Nd and Sm, indicated almost the same result as U, which was about 0.1%. It was suggested that the subcritical water could separate portion of FP. Further study would be carried out with smaller-sized fuel.
Hotoku, Shinobu; Asakura, Toshihide; Mineo, Hideaki; Uchiyama, Gunzo
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 39(Suppl.3), p.313 - 316, 2002/11
no abstracts in English